What is Fucoidan?
Imagine a hidden treasure within the ocean's depths, a natural marvel found in the cell walls of brown seaweed like Mekabu and Mozuku.
Fucoidan is a complex mix of sulfated polysaccharides that boosts your immune system, supports cellular health, and promotes overall wellness.
Harvested from the pristine oceans of Australia, Okinawa, and Patagonia, Fucoidan is sourced from seaweed grown in the cleanest waters.
Its remarkable benefits have been extensively validated by numerous scientists and doctors. Embrace a legacy of wellness with Fucoidan, nature's resilience captured in a supplement designed to elevate your health and unlock the secrets of the sea.
Fucoidan Seaweed
(From Which Seaweed Can Fucoidan Be Extracted?)
Fucoidan is primarily extracted from several types of seaweeds, particularly brown algae. These brown algae are rich in a unique polysaccharide called fucoidan, which is predominantly found in
seaweeds such as Mozuku, Mekabu and Bladderwrack.
These seaweeds are renowned for their high fucoidan content and grow in various regions around the world, including the waters of Japan, Australia, Korea, and Patagonia.

Mozuku (Cladosiphon okamuranus)
Mozuku is primarily harvested in the shallow waters around Okinawa, Japan. It is a staple in the Okinawan diet, contributing to the region's reputation for longevity.
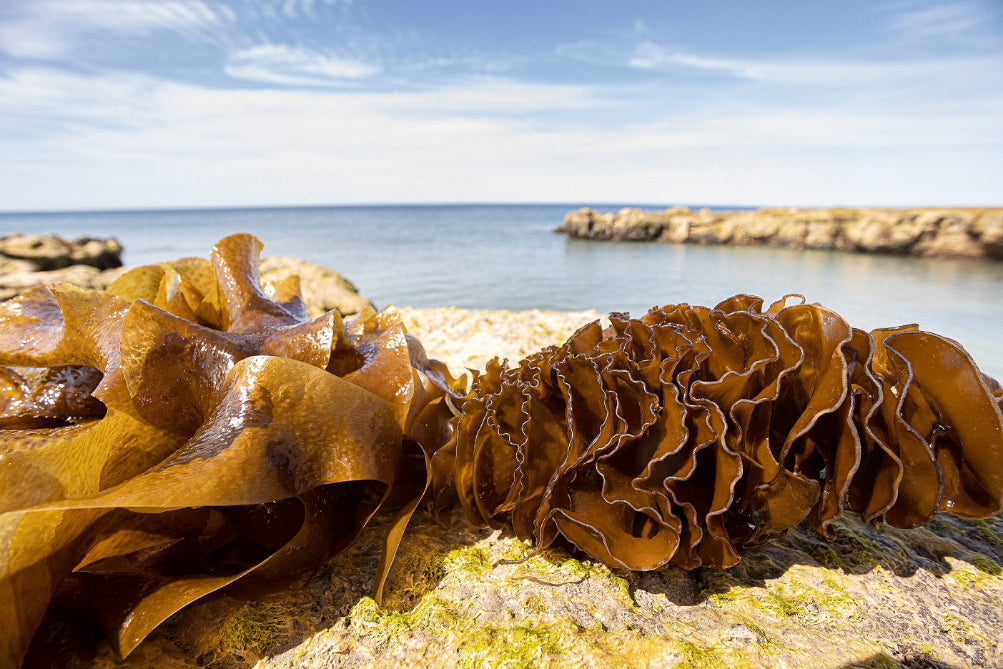

Mekabu (Undaria pinnatifida)
Mekabu is the ruffled, flowering sprout located at the base of the wakame seaweed. One of the unique features of mekabu fucoidan is its high content of sulfated groups, exceeding 34%.
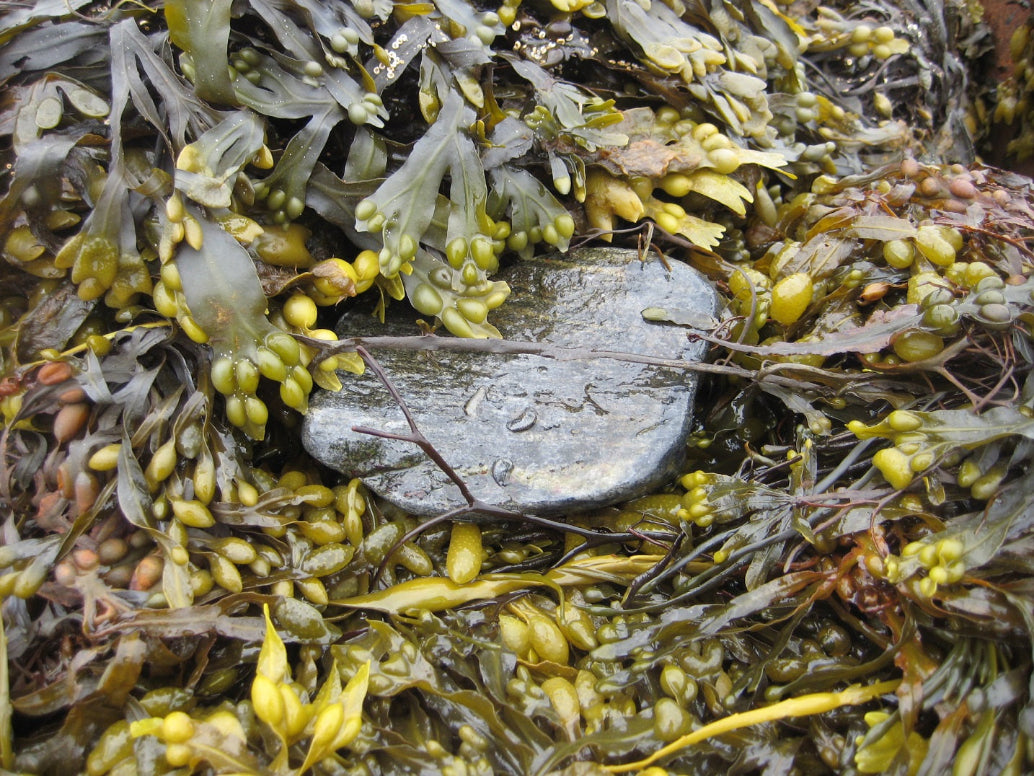

Bladderwrack (Fucus vesiculosus)
Fucus fucoidan has a long history. This fucoidan is extracted from bladderwrack, a type of seaweed found on the coasts of the North Sea, the western Baltic Sea, and the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. The name "Fucus" is derived from the scientific name Fucus vesiculosus, which is the species contained in bladderwrack
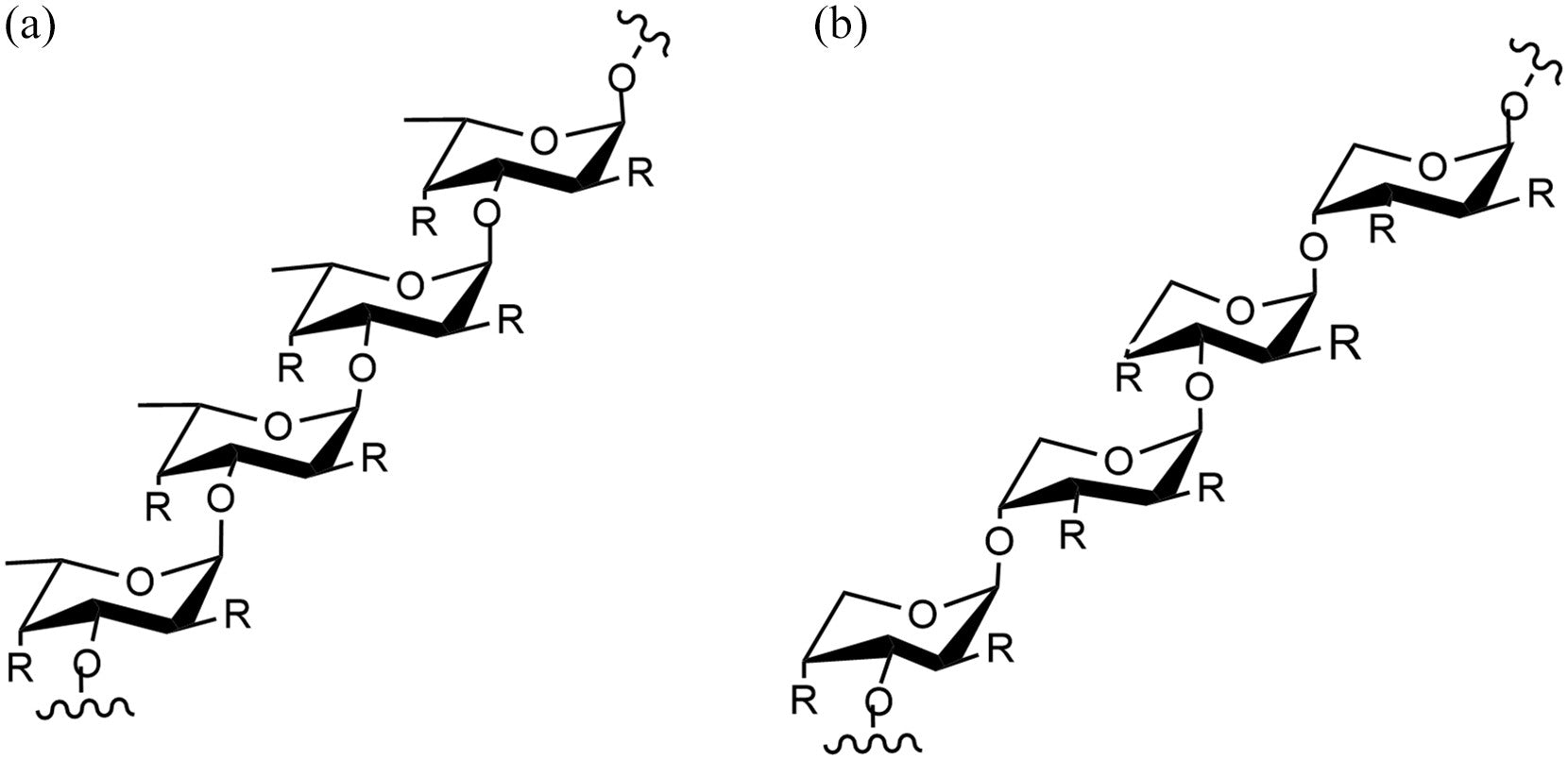
Structure of Fucoidan
Fucoidan is a type of polysaccharide primarily composed of L-fucose and sulfate ester groups, derived from brown seaweed.
Its structure can vary significantly depending on the seaweed species.
Common structural components include monosaccharides like mannose, galactose, glucose, and xylose, along with uronic acids and sometimes acetyl groups and proteins.
-
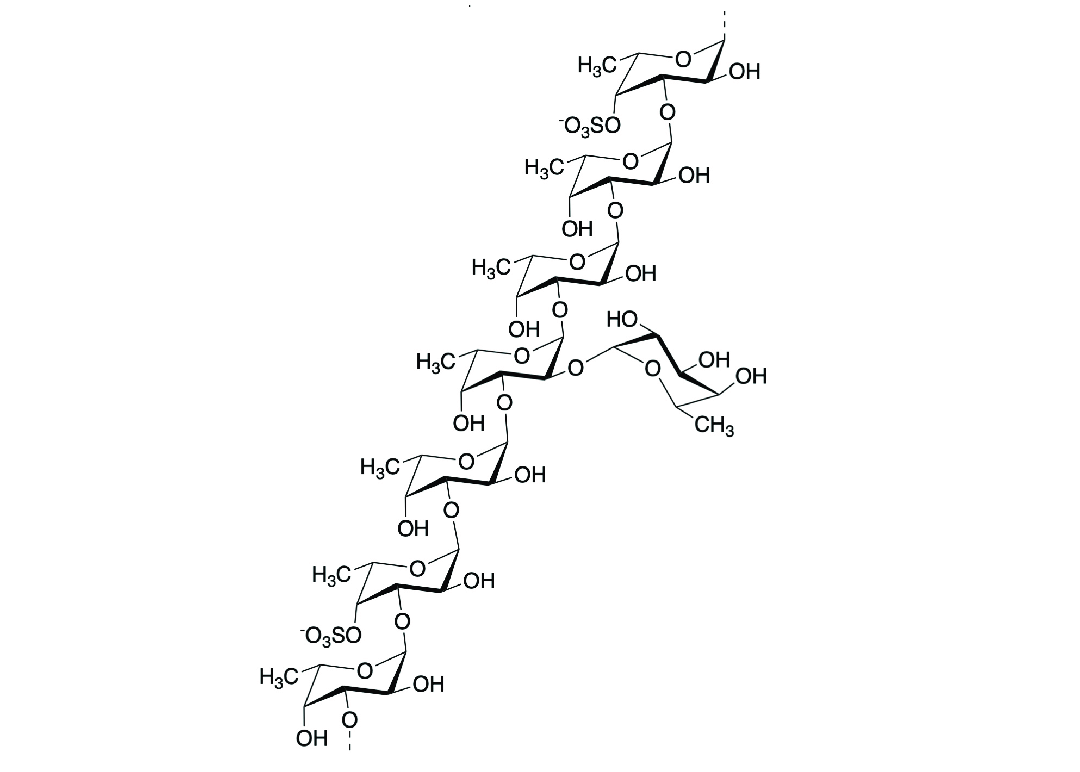
Mozuku (Cladosiphon okamuranus)
-
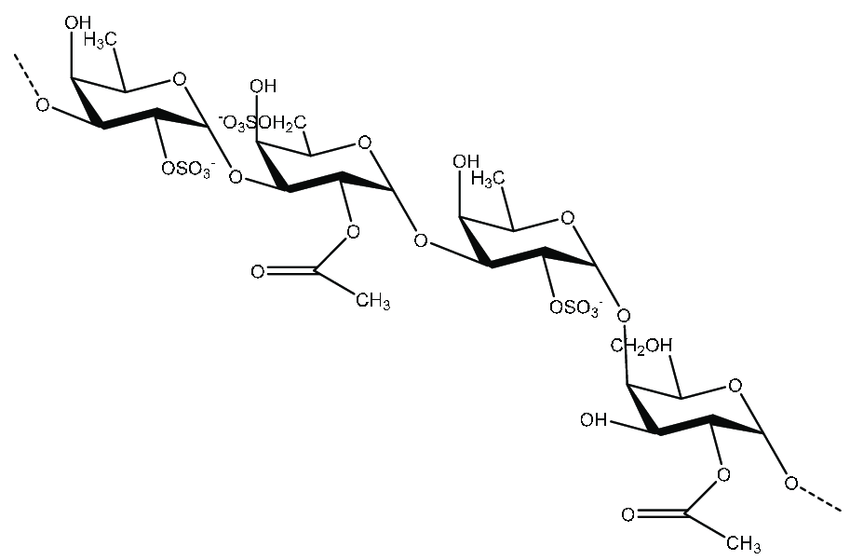
Mekabu (Undaria pinnatifida)
-
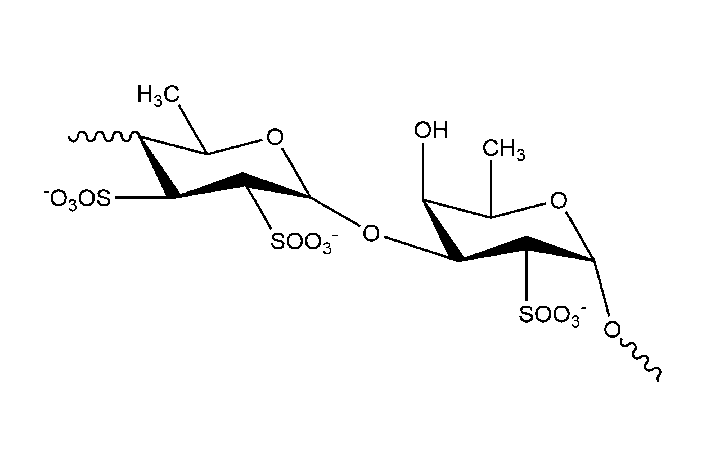
Bladderwrack (Fucus vesiculosus)
The structure of fucoidan varies significantly depending on the type of seaweed from which it is extracted.
Consequently, different types of fucoidan possess distinct properties, leading to varying health benefits.
This means that not all fucoidans have the same effects or health benefits.
Nature Medic's fucoidan products are formulated by combining various types of fucoidan, each with unique characteristics, to create a product with superior efficacy.
High vs. Low Molecular Weight Fucoidan
High molecular weight fucoidan and low molecular weight fucoidan differ structurally in their molecular size. High molecular weight fucoidan has larger, more complex polysaccharide chains, enhancing immune activation and providing superior anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Low molecular weight fucoidan has shorter chains and is absorbed differently.
Nature Medic uses only High Molecular weight Fucoidan to ensure maximum efficacy and health benefits.